Table of contents
In this article, I am going to explain the built-in JavaScript method: Array.map() and then look at a few examples of how to use it.
Introduction
As stated earlier, Map() is a built-in JavaScript method that creates a new array with modified elements, i.e. it allows you to iterate over an array and modify each element using a callback function, then return an array of these modified elements.
Syntax
arr.map(function(currentElement, index, array))
arris the array we are looping throughfunctionis the function to execute for each element of the arraycurrentElementis the value of the current element being processed in the arrayindexis the index of the current element being processedarrayis the array we are looping through
Note:
Map() creates a new array by calling a function for each element of the array
Map() only calls a function once for each element.
Map() does not execute the function for empty elements
Map() does not modify the original array
Examples:
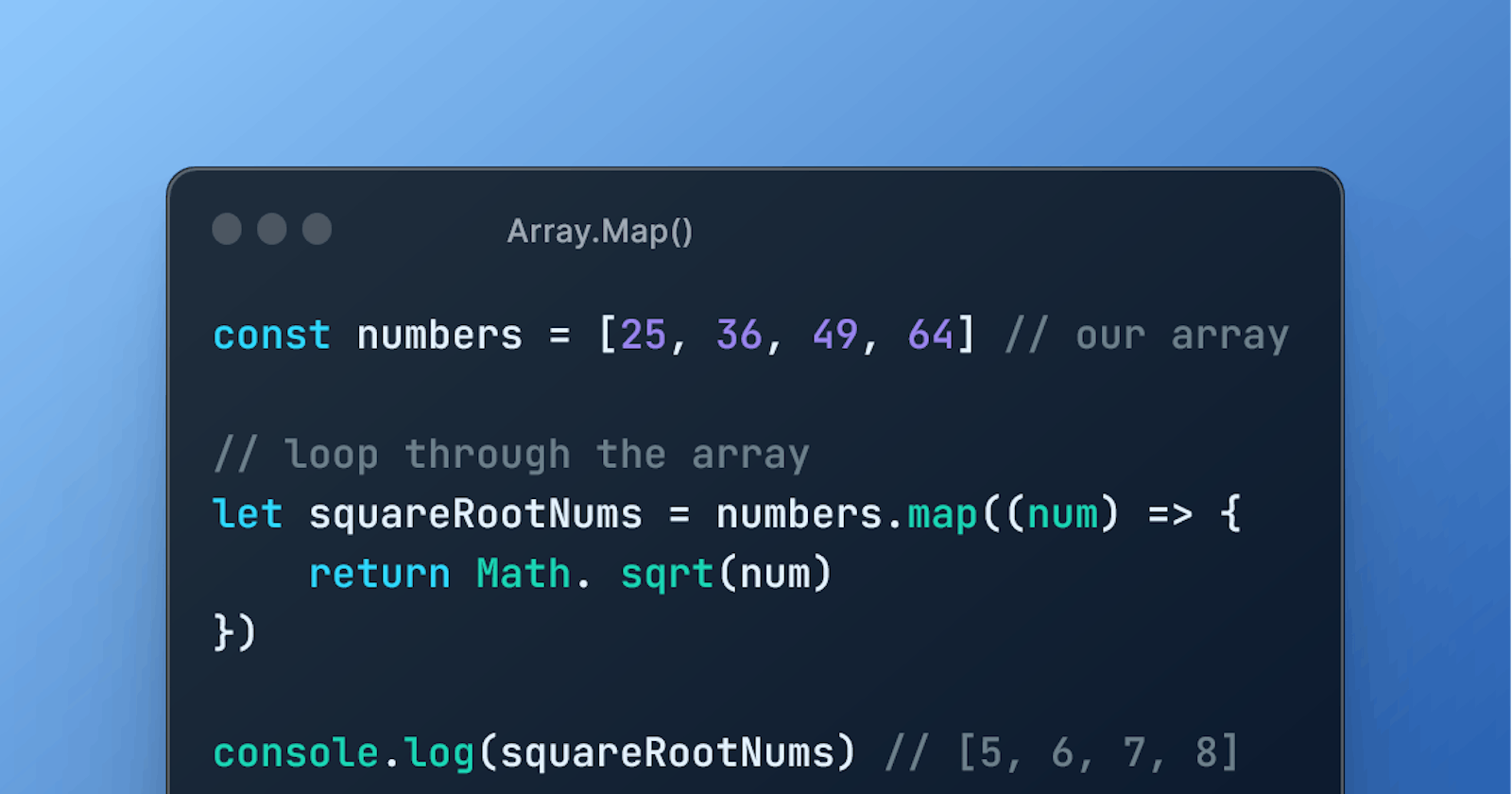
Example 1: Loop through an array of numbers
const numbers = [25, 36, 49, 64] // our array
// loop through the array
let squareRootNums = numbers.map((num) => {
return Math. sqrt(num)
})
console.log(squareRootNums) // [5, 6, 7, 8]
Example 2: Loop through an array of objects
const students = [
{name: 'Pat', grade: 'A'},
{name: 'Enid', grade: 'B'},
{name: 'Kelvin', grade: 'C'},
{name: 'Mercy', grade: 'A'},
]
let newArray = students.map((student) => {
return `${student.name} : ${student.grade}`
})
console.log(newArray) // ['Pat : A', 'Enid : B', 'Kelvin : C', 'Mercy : A']
That's all for this article. Thank you for reading :).
References